| [1]Mao ZW,Shi HF,Guo R,et al.Enhanced angiogenesis of porous collagen scaolds by incorporation of TMC/DNA complexes encoding vascular endothelial growth factor.Acta Biomater.2009;5:2983.[2]Yu H,VandeVord PJ,Mao L,et al.Improved tissue-engineered bone regeneration by endothelial cell mediated vascularization. Biomaterials. 2009;30(4):508.[3]Leung KS,Sber AH,Lam TS,et al.Energy metabolism in fracture healing. Measurement of adenosine triphosphate in callus to monitor progress. J Bone Joint Surg.1989;71B (4):657.[4]Barralet J,Gbureck U,Habibovic P,et al.Angiogenesis in calcium phosphate scaffolds by inorganic copper ion release.Tissue Eng Part A.2009; 15(7):1601. [5]Yoshida T,Kikuchi M,Koyama Y,et al.Osteogenic activity of MG63 cells on bone-like hydroxyapatite/collagen nanocomposite sponges.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2010;21(4): 1263.[6]Gorustovich AA,Roether JA,Boccaccini AR.Effect of bioactive glasses on angiogenesis: a review of in vitro and in vivo evidences.Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2010;16(2):199.[7]Hirschi KK,D'Amore PA.Control of angiogenesis by the pericyte: molecular mechanisms and significance.EXS. 1997;79:419.[8]Bottcher RT,Niehrs C.Fibroblast growth factor signaling during early vertebrate development.Endocrine Rev.2005;26:63.[9]Kanczler JM,Oreffo RO.Osteogenesis and angiogenesis: the potential for engineering bone.Eur Cell Mater.2008;15:100.[10]Lovett M,Lee K,Edwards A,et al.Vascularization strategies for tissue engineering.Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2009;15(3):353.[11]Pacicca DM,Patel N,Lee C,et al.Expression of angiogenic factors during distraction osteogenesis.Bone.2003;33:889.[12]Hofmann A,Ritz U,Verrier S,et al.The effect of human osteoblasts on proliferation and neo-vessel formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells in a long-term 3D co-culture on polyurethane scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2008; 29(31):4217.[13]Santos MI,Unger RE,Sousa RA,et al.Crosstalk between osteoblasts and endothelial cells co-cultured on a polycaprolactone-starch scaffold and the in vitro development of vascularization.Biomaterials.2009;30(26):4407.[14]Deb S,Mandegaran R,Di Silvio L.A porous scaffold for bone tissue engineering/45S5 Bioglass derived porous scaffolds for co-culturing osteoblasts and endothelial cells.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2010;21(3):893.[15]Zhang WB,Shen YH,Pan HB,et al.Effects of strontium in modi?ed biomaterials.Acta Biomater.2011;7:800.[16]Xie H,Wang Q,Ye Q,et al.Application of K/Sr co-doped calcium polyphosphate bioceramic as scaffolds for bone substitutes.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2012;23(4):1033.[17]Zreiqat H,Ramaswamy Y,Wu C,et al.The incorporation of strontium and zinc into a calcium-silicon ceramic for bone tissue engineering.Biomaterials. 2010;31(12):3175.[18]Qianbin W,Qiguang W,Changxiu W.The effect of porosity on the structure and properties of calcium polyphosphate bioceramics.Ceramics Silikáty. 2011;55(1):43.[19]Qianbin W,Qiguang W,Changxiu W.Effect of sintering time on the microstructure and properties of inorganic polyphosphate bioceramics. Science Sintering.2010;42:337.[20]Liu F,Zhang X,Yu XX,et al.In vitro study in stimulating the secretion of angiogenic growth factors of strontium-doped calcium polyphosphate for bone tissue engineering.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2011;22:683.[21]余喜讯,顾志鹏,任大伟,等.新型骨科材料SCPP 对成骨细胞促血管化生长因子表达影响的研究[J].四川大学学报,2011,43(1): 219.[22]Soker S,Machado M,Atala A.Systems for therapeutic angiogenesis in tissue engineering.World J Urol.2000;18:10.[23]Zhang J,Hu M,Zhang WY.Influence of vascular cell co-cultured with osteoblast in vitro on ability of osteoblast.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2005;23:325.[24]Boden SD.Bioactive factor for bone tissue engineering.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1999;(367 Suppl):84.[25]Holliinger JO,Brekke J,Graskin E,el a1.Role of bone substitutes. Clin Orthop.1996;324:55.[26]Coulonbe J,Faure H,Robin B,el a1.In vitro effects of strontium ranelate on the extraccllular calcium sensing receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;323:1184. [27]Tokuda H,Hirade K,Wang X,et al.Involvement of SAPK/JNK in basic fibroblast growth factor-induced vascular endothelial growth factor release in osteoblasts.J Endocrino1.2003; 177(1): 101.[28]傅德皓.骨形态发生蛋白-2诱导成骨过程中血管内皮生长因子的表达及意义[D].华中科技大学博士学位论文,2006.[29]贾健.掺锶硫酸钙复合骨修复材料的体外实验研究[D].四川大学博士学位论文,2007.[30]Jaebong K,Jihjng L,Renhe X,et al.Mesoderm induction by heterodimeric AP-1(c-fos,c-jun) and its involvement in mesoderm formation through the embryonic fibroblast growth factor/xbra autocatalytic loop during the early development of Xenopus embroes.J Biol Chem.1998;272:1542.[31]Galoforo SS,Bernslm,Erdos G,et al.Hypoglycemia-induced AP-1 transcription factor and basic fibriblast growth factor gene expression in multidrug resistant human breast carcinoma MCF-7/ADR. Cells Mol Cell Biochem,1996;155: 163. |
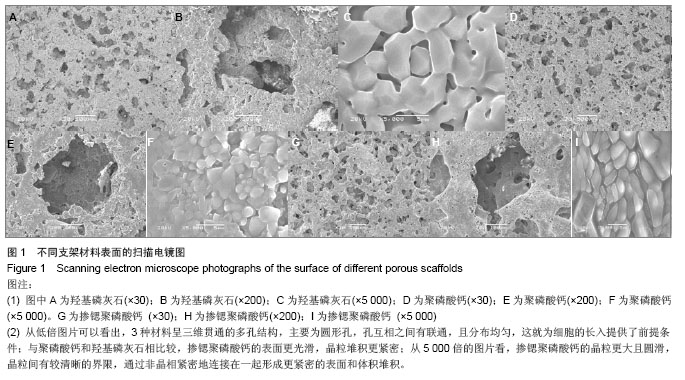
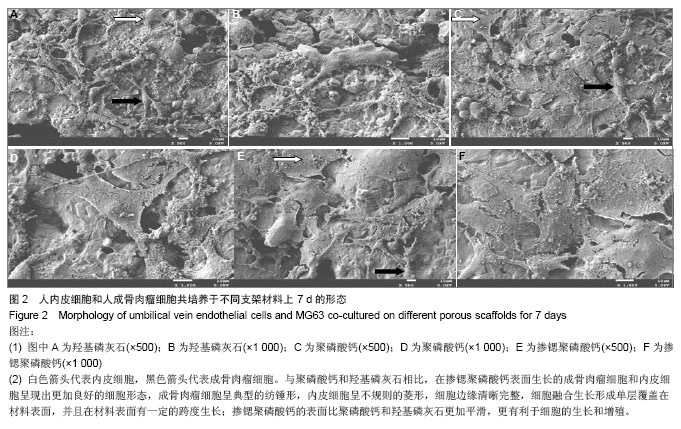
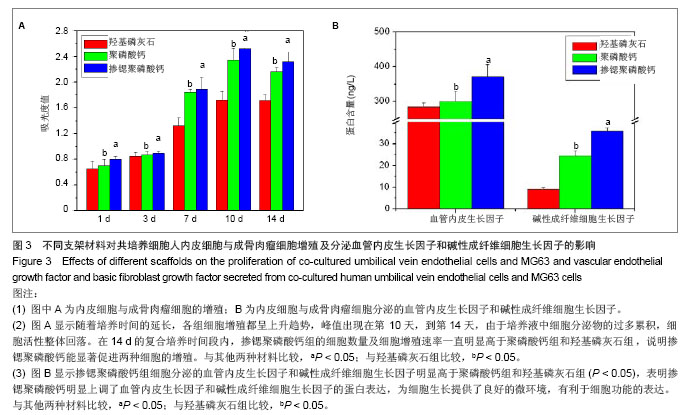
.jpg)